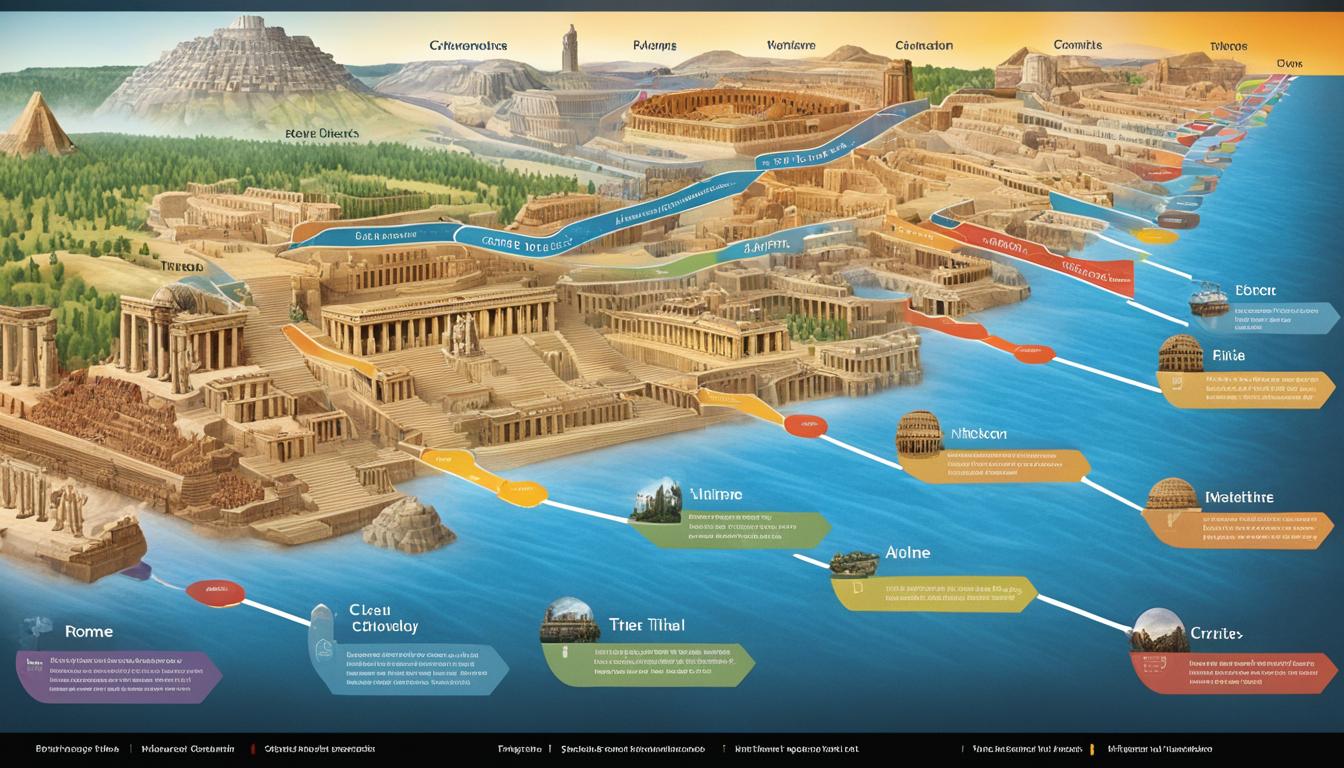
Welcome to the fascinating world of ancient civilizations! Step back in time and uncover the wonders of our ancestors through the ancient civilizations timeline. This comprehensive timeline chronicles the documented history of ancient societies, from the dawn of civilization to the Early Middle Ages.
Delve into the rich tapestry of human history and witness the rise and fall of great empires, the development of groundbreaking technologies, and the flourishing of remarkable art and culture.
Embark on a journey that takes you from the fertile lands of Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, to the magnificent pyramids of Ancient Egypt. Explore the engineering marvels of the Incan civilization and the architectural brilliance of the Aztecs. Marvel at the glories of the Roman Empire and the intellectual achievements of Ancient Greece. Discover the vast Persian Empire and its impressive Royal Road network.
Key Takeaways:
- Gain insights into the timeline of ancient civilizations, spanning from the earliest recorded history until the Early Middle Ages.
- Discover the fascinating achievements and contributions of ancient civilizations such as the Inca, Aztec, Roman, Persian, and Greek societies.
- Explore the architectural wonders, engineering excellence, and cultural advancements of ancient civilizations.
- Learn about the birth of writing systems, the development of complex societies, and the establishment of influential political and governing systems.
- Appreciate the enduring impact of ancient civilizations on our modern world, as their legacies continue to shape and inspire us today.
Immerse yourself in the captivating stories and remarkable achievements of our ancient predecessors. Begin your journey through time and delve into the ancient civilizations timeline now!
Incan civilization – pottery remains
The Inca people, from 1438 to 1532, established themselves as South America’s largest empire during the pre-Columbian era. Known for their engineering excellence, the Incan civilization achieved remarkable feats in architecture and construction, with one notable example being the awe-inspiring city of Machu Picchu.
Machu Picchu, located in the Andes Mountains of modern-day Peru, served as a magnificent urban settlement and a testament to the Inca’s ingenuity. This ancient city was built using advanced engineering techniques, with its stone structures crafted to withstand the test of time and the formidable elements of the mountainous region. The precision and skill demonstrated in the construction of Machu Picchu exemplify the engineering mastery of the Incan civilization.
However, pottery remains also shed light on the daily lives and cultural practices of the Inca people. Pottery, a significant aspect of Incan art, was used for utilitarian purposes as well as for ceremonial and religious rituals. Incan pottery was intricately designed and often depicted symbolic representations of their beliefs, traditions, and natural surroundings.
Pottery as a Cultural Artifact
The pottery of the Inca civilization serves as a valuable archaeological artifact, providing insights into their craftsmanship, artistic expressions, and social customs. Each piece of pottery represents a unique fusion of aesthetic beauty, functional design, and cultural significance.
“Incan pottery reflects an exceptional level of artistry and craftsmanship. The intricate designs and vibrant colors used by Inca artisans are a testament to their creativity and attention to detail.”
By examining the pottery remains, archaeologists and historians have been able to gain a deeper understanding of the Inca people’s daily lives, including their agricultural practices, food storage techniques, and even the types of foods consumed during different periods. Pottery fragments have also provided valuable evidence of trade networks, as distinct styles and designs have been found in different regions.
The utilization of advanced engineering in the construction of Machu Picchu, combined with the artistic and cultural expressions found in Incan pottery, showcases the remarkable achievements and cultural richness of the Inca civilization.
| Key Characteristics of Incan Civilization |
|---|
| Advanced engineering techniques |
| Construction of Machu Picchu |
| Intricately designed pottery |
| Symbolic representations of beliefs and traditions |
| Insights into daily lives and cultural practices |
| Evidence of trade networks |
Join us as we continue our journey through the timeline of ancient civilizations, exploring the achievements, advancements, and legacies left behind by these remarkable societies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fF0lhuX5sOI
Aztec Stone Coatlique (Cihuacoatl) Earth Goddess
The Aztecs, from 1325 to 1521, established the formidable Aztec civilization in South-central Mexico. They created an advanced and complex society that excelled in various domains such as agriculture, art, architecture, politics, and military strategies.
The Aztecs constructed their capital city, Tenochtitlan, on an island in Lake Texcoco. With its intricate layout and impressive infrastructure, Tenochtitlan showcased the urban planning skills and engineering prowess of the Aztec civilization. The city featured causeways, canals, and stone-paved roads that symbolized their expertise in hydraulic engineering.
Driven by innovative agricultural practices, the Aztecs implemented a floating garden system called chinampas. These artificial islands cultivated on the lake allowed for high crop yields and sustained the growing population of the city.
The Aztec society was highly stratified, with an elaborate social structure dominated by nobles, warriors, priests, and commoners. Their political system centered around an emperor who held absolute power and served as the religious leader as well.
Art and architecture played a significant role in Aztec culture. The Aztecs created stunning sculptures, intricate jewelry, and vibrant murals, often depicting their gods and goddesses. One notable representation is the Aztec Stone Coatlique, also known as Cihuacoatl, the Earth Goddess.
“The Aztec civilization represents a pinnacle of human achievement in the ancient world. Their advancements in various fields and the grandeur of Tenochtitlan make them one of the most sophisticated civilizations of their time.”
Despite their cultural achievements, the Aztecs were also known for their military might and expansionist ambitions. Through strategic alliances, military campaigns, and tribute systems, the Aztec empire expanded its influence over neighboring regions, establishing a vast and powerful dominion.
The Aztec civilization was eventually conquered by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés and his army in 1521. The fall of Tenochtitlan marked the end of the Aztec empire and the beginning of Spanish colonial rule in Mexico.
Discover more about the fascinating Aztec civilization, their achievements, and their ultimate demise in the following table:
| Aspects of Aztec Civilization | Notable Examples |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Chinampas (floating gardens) |
| Art and Architecture | Aztec Stone Coatlique, Templo Mayor |
| Political System | Emperor, nobles, warriors |
| Military Strategies | Strategic alliances, tribute systems |
| Conquest | Spanish Conquest, Fall of Tenochtitlan |
Immerse yourself in the rich cultural heritage and astounding achievements of the Aztec civilization by exploring their art, architecture, and remarkable city of Tenochtitlan.

Roman Empire around 117 AD
The Roman Empire, spanning from 753 BC to 476 AD, was a dominant force that shaped the course of history. This mighty civilization expanded its reach across Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia, leaving a lasting legacy that still influences our world today. One of the most iconic symbols of Roman ingenuity and grandeur is the Colosseum.
The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre, stands as a testament to the architectural brilliance of the Romans. This colossal structure, located in the heart of Rome, was an arena dedicated to hosting gladiatorial contests, public spectacles, and theatrical performances. With its intricate design and capacity to hold up to 50,000 spectators, the Colosseum remains an iconic symbol of Roman entertainment and culture.
Another architectural marvel of the Roman Empire is the Pantheon. Built in 126 AD, the Pantheon is a stunning example of Roman engineering and religious devotion. This temple, dedicated to the worship of all gods, features a massive domed roof supported by ancient columns. The oculus, a circular opening at the top of the dome, allows natural light to illuminate the interior, creating a breathtaking effect. The Pantheon continues to awe visitors with its timeless beauty and remarkable architectural achievements.
“Rome – the city of visible history, where the past of a whole hemisphere seems moving in funeral procession with strange ancestral images and trophies gathered from afar.”
Notable Achievements of the Roman Empire
- Establishment of a vast network of roads, including the famous Appian Way, to facilitate trade and communication.
- Advancement in engineering with the creation of aqueducts, enabling the supply of water to major cities.
- Development of a comprehensive legal system known as Roman Law, which greatly influenced the legal systems of modern societies.
- Promotion of education and learning through the construction of libraries and schools.
| Area of Achievement | Symbol of Roman Empire |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Colosseum and Pantheon |
| Military | Legionary Eagle |
| Engineering | Aqueducts |
| Government | Senate |
| Law | Justinian Code |
The remains of Persepolis – an ancient Persian city
Explore the fascinating remains of Persepolis, an ancient city that once flourished as the capital of the mighty Persian Empire. Built between the 6th and 4th centuries BC, Persepolis stood as a testament to the grandeur and power of the Persian civilization.
One of the most striking features of Persepolis is the Royal Road, a remarkable accomplishment of engineering that connected the vast territories of the Persian Empire. This network of paved roads spanned over 1,500 miles, facilitating trade and communication between the empire’s cities and regions.
The Royal Road played a vital role in the prosperity and expansion of the Persian Empire. It allowed for the efficient movement of not only goods and resources but also messengers and armies. The road was equipped with stations where travelers could rest and exchange horses, ensuring a speedy and reliable transportation system.
Persepolis itself was a magnificent city, filled with impressive palaces, monumental staircases, and exquisite sculptures. It served as a center of administration and ceremonial gatherings, where kings received tribute from their subjects and hosted lavish festivities.
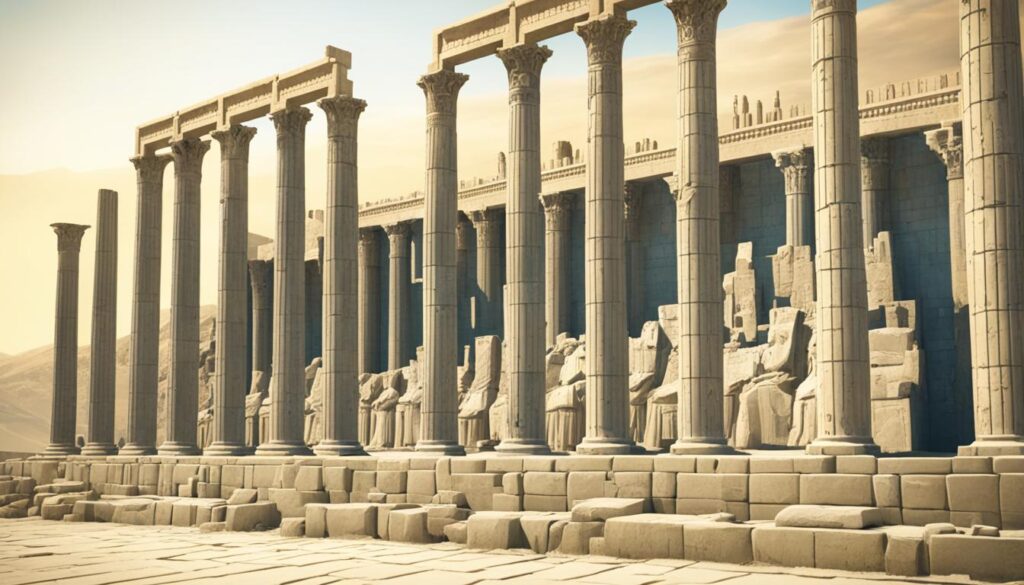

As you explore the remains of Persepolis, you’ll be transported back in time to an era of opulence and power. The intricate carvings and elaborate architecture will leave you in awe of the Persian Empire’s achievements and cultural richness.
While Persepolis may now be in ruins, it serves as a testament to an empire that once dominated the ancient world. So take a step into history and immerse yourself in the grandeur of the Persian civilization at the remains of Persepolis.
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece, from 2700 BC to 479 BC, was a cultural and intellectual powerhouse that left an indelible mark on human history. It was a period of remarkable achievements in art, science, technology, literature, philosophy, and politics.
One of the most significant contributions of Ancient Greece was the development of democracy. The concept of democracy, derived from the Greek words “demos” (people) and “kratos” (rule), gave power to the citizens to participate and make decisions in the governance of their city-states. This revolutionary system laid the foundation for modern democratic societies.
Ancient Greece is also renowned for the Olympic Games, a tradition that continues to this day. The Olympics, held every four years in Olympia, celebrated athletic excellence and promoted peace among the city-states. Athletes from different regions would compete in events such as running, wrestling, and chariot racing, showcasing their physical abilities and sporting prowess.
Ancient Greek society valued knowledge and education. Scholars and philosophers, such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, explored various fields of study, including philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Their theories and teachings continue to influence modern thought and provide insights into the nature of the world and the human condition.
“The ancient Greeks have a vital message to convey in this critical moment. They remind us of the courage it takes to pursue both intellectual and physical excellence, the power in unity and equality, and the transformative potential of democracy.”
– Dr. Sophia Rodriguez, Professor of Ancient History
Ancient Greece at a Glance:
| Key Aspects | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Governance | Foundation of democracy |
| Athletics | Olympic Games |
| Arts & Sciences | Contributions to philosophy, literature, mathematics, and more |
Ancient Greece, with its democratic ideals, transformative sporting events, and intellectual achievements, continues to inspire and shape the world we live in today.
Mesopotamia – the cradle of civilization
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, holds the title of being the birthplace of civilization. It was in this region, from 3500 BC to 2375 BC, that many significant advancements and innovations emerged. The Sumerians, the early inhabitants of Mesopotamia, played a crucial role in shaping the course of human history through their contributions in several fields.
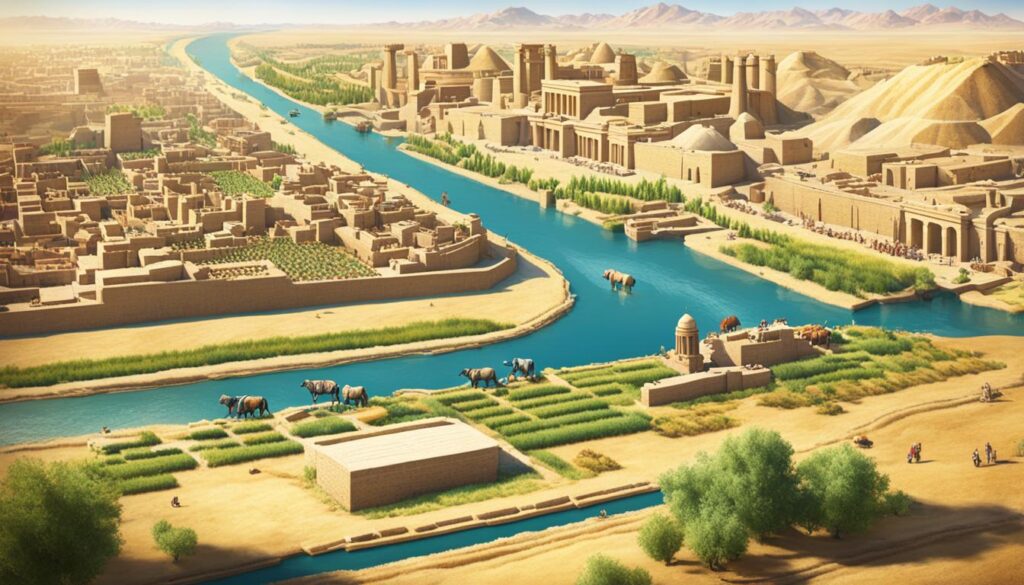
Sumerians: Trailblazers of Progress
The Sumerians excelled in various areas, including agriculture, metalworking, mathematics, and governance. Their advanced agricultural techniques allowed them to cultivate crops and sustain large populations, leading to the establishment of some of the world’s first cities. Additionally, their mastery of metalworking enabled the creation of tools and weapons, which further contributed to their cultural and economic development.
Unlocking the Secrets of Cuneiform Writing
One of the Sumerians’ most significant achievements was the development of cuneiform writing, the earliest known form of writing in human history. This revolutionary system involved making impressions on clay tablets using a stylus, resulting in wedge-shaped symbols representing words and concepts. Cuneiform allowed for the recording of laws, literature, and historical events, ensuring the preservation of knowledge for future generations.
“The invention of cuneiform writing by the Sumerians revolutionized communication and laid the foundation for written language as we know it today.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Archaeologist
The advent of writing not only facilitated record-keeping but also allowed for the dissemination of ideas, advancements, and cultural practices across Mesopotamia and beyond. It paved the way for the development of complex societies, the establishment of legal systems, and the growth of trade networks.
The Legacy of Mesopotamia
The contributions of Mesopotamia and the Sumerians have left an indelible mark on human civilization. Their inventions and innovations laid the groundwork for the development of subsequent ancient civilizations, shaping the course of history. From the agricultural techniques that transformed subsistence farming to the invention of writing that revolutionized communication, their achievements continue to influence our lives today.
| Contributions of the Sumerians | Impact |
|---|---|
| Agricultural advancements | Enabled the growth of cities and the establishment of complex societies |
| Mastery of metalworking | Contributed to technological progress and economic development |
| Development of cuneiform writing | Revolutionized communication and paved the way for the spread of knowledge |
Ancient Egypt and the Nile River
Ancient Egypt, from 5000 BC to 30 BC, was a civilization that thrived along the banks of the Nile River. The Nile River was the lifeblood of this ancient civilization, providing sustenance, transportation, and a constant water supply. The Egyptians recognized the importance of this mighty river and its annual flooding, which enriched the soil and allowed for successful agricultural practices.
One of the most iconic aspects of Ancient Egypt is the construction of magnificent pyramids. These monumental structures served as tombs for pharaohs and were built with astonishing precision and engineering skills. The pyramids are a testament to the advanced architectural abilities and the complex religious beliefs of the ancient Egyptians.
“The Nile, with its annual floods, was the cradle of Ancient Egypt’s civilization.”
Ancient Egyptians developed a complex and sophisticated culture that encompassed art, literature, religion, and social hierarchies. They believed in the afterlife and dedicated significant resources and efforts to ensure a smooth transition for their rulers. The elaborate burial rituals, intricate hieroglyphic writings, and majestic temples are a testament to the rich cultural heritage of Ancient Egypt.
Furthermore, the Egyptian civilization left a lasting legacy in the field of mathematics, medicine, and astronomy. Their advancements in these areas continue to influence the modern world.
The Nile River, with its life-giving properties, allowed Ancient Egypt to prosper for thousands of years. It shaped the society, economy, and culture of this remarkable civilization. The pyramids stand as a testament to the ingenuity and grandeur of Ancient Egypt, captivating the imagination of people around the world to this day.
The Agricultural Revolution
The Agricultural Revolution, a turning point in human history, started around 6500 BC.
During this period, significant changes occurred in farming practices and technology, leading to the development of permanent settlements and groundbreaking inventions that revolutionized the way people lived.
Farming Innovations
One of the key aspects of the Agricultural Revolution was the invention of new farming techniques. Farmers discovered the benefits of crop rotation, allowing them to maintain soil fertility and increase productivity. By alternating crops seasonally, they prevented soil depletion and created more sustainable agricultural systems.
In addition, farmers began to cultivate plants selectively, focusing on species that yielded more food or had favorable qualities. This process, known as selective breeding, resulted in the domestication of plants and animals, leading to increased food production and the establishment of sedentary communities.
Another significant development was the utilization of irrigation systems to control the water supply for crops. People built canals, ditches, and reservoirs to capture and distribute water, ensuring reliable irrigation even in arid regions. This advancement played a crucial role in supporting larger populations and expanding agricultural production.
Furthermore, the invention of the plow transformed farming practices. The plow allowed farmers to break up the soil, making it easier to sow seeds and control weeds. It increased efficiency and productivity, enabling farmers to cultivate larger areas of land and produce surplus food.
The Impact of the Agricultural Revolution
The Agricultural Revolution brought about significant societal changes. The transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled farming communities led to the development of permanent housing and the establishment of villages and towns.
This shift also had a profound impact on social structures. With the surplus food generated by agriculture, specialized labor emerged, creating a division of labor within communities. Some individuals focused on farming, while others pursued specialized trades such as pottery-making, metalworking, or weaving.
Moreover, the increased food production resulted in population growth. As societies became more settled, populations could sustain themselves better, leading to larger communities and urbanization.
The innovations of the Agricultural Revolution also paved the way for technological advancements in various fields. Metalworking, for instance, allowed for the development of new tools and weapons. Writing systems emerged as a means of record-keeping and communication, providing a foundation for the advancement of knowledge and civilization.
Overall, the Agricultural Revolution transformed human societies by enabling greater food security, sedentary living, and the rise of civilization. It laid the groundwork for future advancements in farming and technology, setting the stage for the development of complex, organized societies.

The Impact of the Agricultural Revolution
| Impact of the Agricultural Revolution | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased food production | The agricultural advancements allowed for greater food production, resulting in improved nutrition and the ability to support larger populations. |
| Establishment of permanent settlements | The shift from nomadic lifestyles to sedentary farming communities led to the development of permanent housing and the establishment of villages and towns. |
| Division of labor | The surplus food generated by agriculture enabled specialization in different trades and professions, leading to a division of labor within communities. |
| Technological advancements | The agricultural revolution laid the foundation for technological advancements in various fields, including metalworking and the development of writing systems. |
Conclusion
In summary, the Ancient Civilizations Timeline provides a comprehensive overview of the development and achievements of various ancient societies. From the Incan civilization’s engineering excellence displayed in the construction of Machu Picchu, to the advanced society built by the Aztecs in Tenochtitlan, these ancient civilizations have left an indelible mark on history.
The Roman Empire, with its monumental architecture such as the Colosseum and the Pantheon, stands as a testament to the power and grandeur of the ancient world. The Persian Empire’s Royal Road, a network of paved roads, facilitated trade and communication across vast distances.
Ancient Greece, the birthplace of democracy and the Olympics, was a beacon of intellectual and cultural achievements. Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, gave rise to the Sumerians and their innovative contributions, including cuneiform writing. And let’s not forget the magnificent civilization of Ancient Egypt, with its awe-inspiring pyramids along the Nile River.
The timeline of ancient civilizations is a reminder of the ingenuity, complexity, and artistic brilliance of these societies. As we delve into ancient history, we gain a deeper understanding of our own civilization’s roots and the lasting impact of those who came before us.